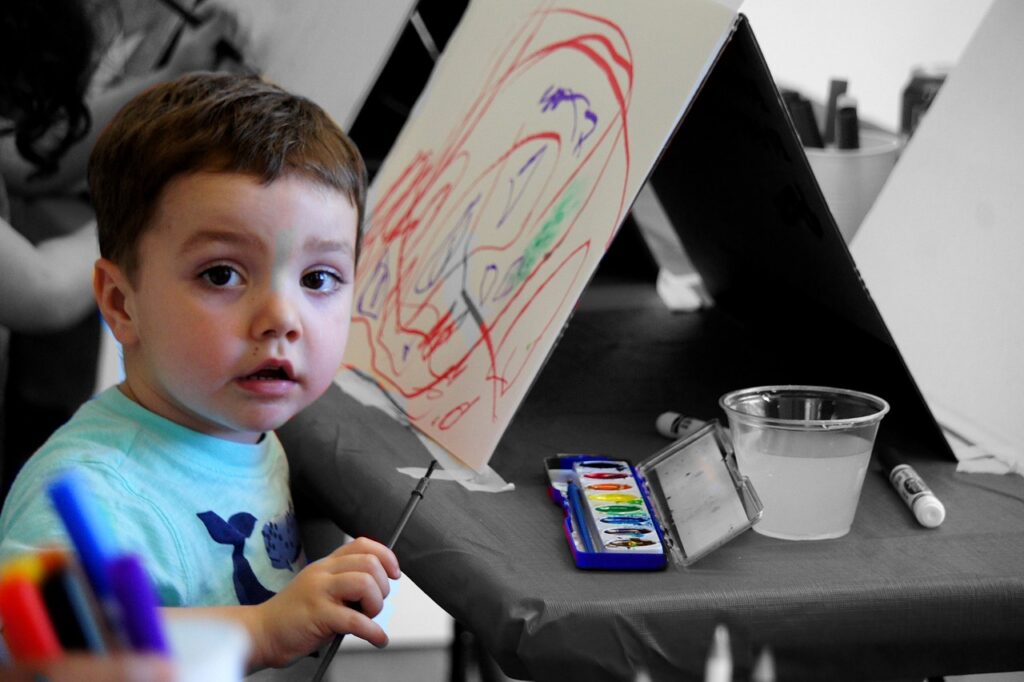
In the world of education, acceptance and support for diverse learning needs have become paramount. One such area that has gained significant attention is the realm of ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). With the implementation of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), accommodations for students with ADHD have become more accessible, ensuring that every child has the opportunity to thrive academically and emotionally. In this article, we will explore the importance of IDEA, the significance of accommodations, and the role of therapy, especially Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and family therapy, in navigating the challenges associated with ADHD. Additionally, we will delve into the complex issues of impulsive behavior, binge eating, emotional outbursts, and the concept of ADHD superpowers, as advocated by publications like Additude Magazine, highlighting the power of acceptance.
IDEA and Accommodations
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a landmark legislation in the United States that ensures students with disabilities, including ADHD, receive a free and appropriate public education tailored to their specific needs. Under IDEA, students diagnosed with ADHD are eligible for accommodations in schools. These accommodations can range from extended time on tests, preferential seating, use of assistive technology, and even individualized education programs (IEPs) tailored to address their unique challenges. IDEA not only provides necessary resources but also fosters an inclusive environment, allowing students with ADHD to participate actively and comfortably in the educational process.
ADHD and Therapy Approaches
CBT for ADHD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used therapeutic approach for managing ADHD. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative patterns of thinking and behavior. In the context of ADHD, CBT helps individuals recognize impulsive thoughts and actions, teaching them coping strategies and impulse control techniques. Through CBT, individuals with ADHD can gain a better understanding of their condition, enhancing their ability to manage impulsivity and hyperactivity effectively.
Family Therapy
ADHD doesn’t just affect the individual; it impacts the entire family dynamic. Family therapy plays a crucial role in providing support and understanding for both the individual with ADHD and their family members. By involving the family in therapy sessions, communication improves, and coping mechanisms are developed collectively. Family therapy sessions offer a safe space for open dialogue, allowing family members to express their concerns, fears, and frustrations, fostering empathy and strengthening familial bonds.
Addressing Impulsive Behavior, Binge Eating, and Emotional Outbursts
Impulsive Behavior
Impulsivity is a common trait associated with ADHD, often leading to impulsive decision-making and actions. Therapy, especially CBT, equips individuals with ADHD with strategies to manage impulsive behavior. Techniques such as mindfulness, self-awareness exercises, and impulse control training empower individuals to pause, evaluate situations, and make conscious decisions, mitigating impulsive tendencies.
Binge Eating
Binge eating, a form of impulsive behavior, can be particularly challenging for individuals with ADHD. Therapy interventions like Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) have shown effectiveness in addressing binge eating behaviors. DBT focuses on enhancing emotional regulation skills, distress tolerance, and mindfulness, providing individuals with ADHD the tools to manage emotional triggers that often lead to binge eating episodes.
Emotional Outbursts
Emotional outbursts are another manifestation of ADHD, often triggered by frustration, overwhelm, or sensory overload. Therapy, including CBT and mindfulness-based interventions, helps individuals identify the root causes of these emotional outbursts. By developing emotional regulation techniques and improving self-awareness, individuals can gain control over their emotions, leading to healthier coping mechanisms and improved social interactions.
ADD/ADHD Superpowers and Acceptance
In recent years, the concept of ADHD superpowers has gained prominence, especially through platforms like Additude Magazine. This perspective focuses on reframing ADHD traits as unique strengths rather than mere challenges. Many individuals with ADHD exhibit remarkable creativity, hyperfocus, and intuitive problem-solving abilities. Embracing these traits as superpowers fosters self-acceptance and self-esteem, enabling individuals to harness their strengths and excel in various areas of life.
Acceptance is a cornerstone in the journey of individuals with ADHD. Acknowledging one’s unique abilities and challenges, and embracing them without judgment, creates a foundation for personal growth and resilience. Therapy, in conjunction with acceptance-based approaches, provides individuals with ADHD the support they need to navigate the complexities of school, relationships, and self-discovery.
Navigating ADHD in the educational system can be a challenging yet transformative journey, one that is significantly enhanced through the implementation of IDEA, appropriate accommodations, and therapeutic interventions like CBT and family therapy. By addressing impulsive behavior, binge eating, and emotional outbursts, individuals with ADHD can develop essential skills to manage their symptoms effectively.
The paradigm shift toward recognizing ADHD traits as superpowers and promoting acceptance brings a sense of empowerment and self-worth. As society continues to embrace neurodiversity, it is crucial to provide a supportive environment where individuals with ADHD can thrive, learn, and contribute meaningfully.