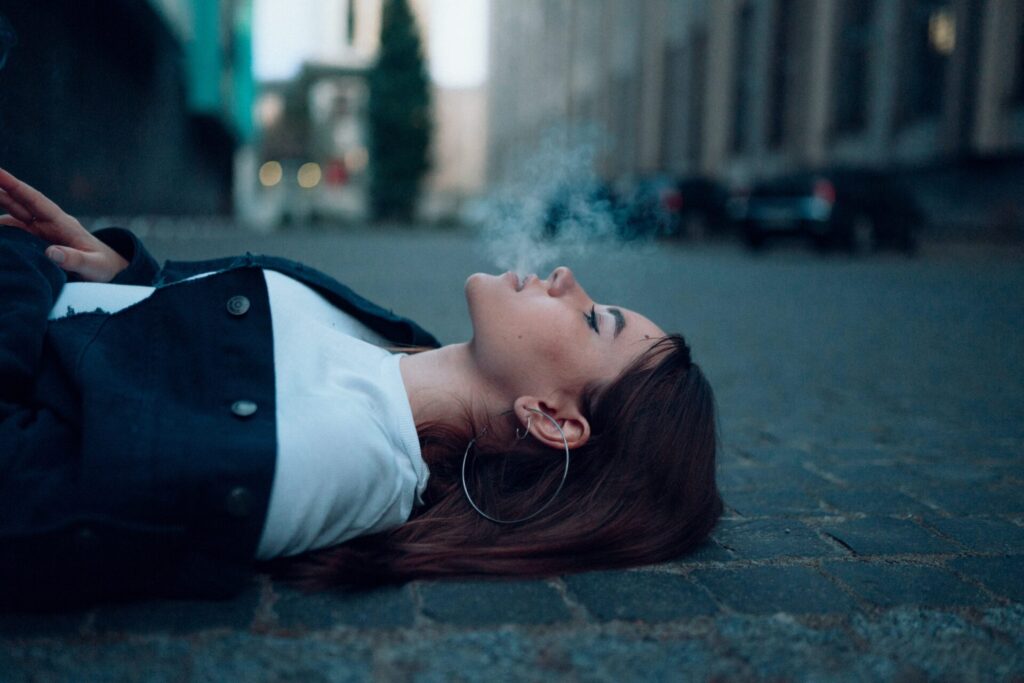
A smoking addiction or nicotine addiction is when you find yourself craving nicotine and can’t stop using it. The powerful addictive chemical is what makes it difficult to give up smoking. Nicotine produces pleasant feelings in your brain — but these feelings are only temporary. When they’ve worn off, you reach for another cigarette to recreate the feeling.
The more you smoke, the more nicotine you need to consume to feel good. When you first try to stop smoking, it’s common to experience unpleasant physical and mental changes. These are caused by your body and mind going through nicotine withdrawal.
Whether you’ve smoked for one month or all your life, quitting cigarettes can improve your health. It certainly isn’t easy, but it’s definitely possible to stop your nicotine dependence. The first step to quitting is to admit that you have an addiction and you need to stop for your health and the health of those around you.
Effects of nicotine addiction
If you’re a smoker, you’ll know that smoking makes you feel good. When you inhale tobacco, your brain releases a number of neurotransmitters, including dopamine — the feel-good chemical. Dopamine is what makes you feel happy and content for a short time.
The problem is that cigarettes don’t only contain nicotine. Cigarettes have many harmful chemicals and cancer-causing agents. There are almost 4,000 individual chemicals in tobacco, each of which has a mental, physical, or psychological effect. Regularly using tobacco can result in all kinds of health complications, including:
- Emphysema
- Lung cancer
- Chronic bronchitis
- Leukemia and other kinds of cancer
- Stroke
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Eye issues, including macular degeneration and cataracts
- Impotence
- Infertility
- Pregnancy complications and miscarriage
- Cold, flu, and respiratory infections
- Weak immune system
- Loss of smell and taste
- Premature aging
- Dental issues and gum disease
- Osteoporosis
- Peptic ulcer disease
Secondhand smoke
When you smoke, it’s not only your own health that is affected. Secondhand smoke dramatically increases the risk of heart disease and lung cancer in people who are physically close to smokers. Children who live with smokers are more likely to develop:
- Asthma
- Sudden infant death syndrome
- Ear infections
- Respiratory infections
- Other related illnesses
Overcoming addiction
The physical part of nicotine addiction can be difficult to manage. To be successful, you need to fully commit to changing your routines and behaviors. There are several treatment options for smoking addiction, including support groups, medication, and therapy.
Support groups
Support groups can help you meet other people in the same situation as yourself. You can share stories and give advice to each other about things that have worked for you. Joining a support group helps you to be accountable and can motivate you to quit.
Medication
There are many different kinds of medication that can help you quit smoking. They work by reducing your cravings. Nicotine inhalers, nasal sprays, lozenges, gums, and patches work by providing your body with nicotine without the other chemicals present in tobacco. Nicotine replacements let you overcome your addiction at a pace that suits you.
Therapy
Therapy can help you develop the coping skills you need to overcome your addiction. Your therapist can help you work through your problems and help you get to the root of your addiction. They can also help you with any other symptoms you experience when you’re quitting, such as stress, depression, and anxiety.
Other solutions
There isn’t a single way to beat your nicotine addiction. While most of the work will involve nicotine replacements, working through withdrawal symptoms, and learning coping skills, there are a few things that can make your move away from nicotine a little easier:
- Enjoy snacks that keep your hands and mouth busy
- Commit to a regular workout schedule
- Avoid situations that are likely to lead to a relapse
- Get rid of tobacco products from your car, home, and place of work
- Be realistic about your treatment
- Set small goals and reward yourself when you achieve them
Withdrawal
Withdrawal is something you need to anticipate when giving up smoking. If you’re addicted to nicotine, you’re almost guaranteed to face withdrawal symptoms when you decide to give up. As you wean your body off the substance, you may experience any of the following:
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Anxiety
- Irritability
You’ll experience the worst withdrawal symptoms during the first seven days. But with every day that passes, it will become easier to avoid cigarettes. After your withdrawal symptoms have gone away, you may experience sudden, random cravings. These can last anywhere from months to years. It’s essential that you learn to be strong and overcome your cravings during these situations.
Your future can be bright
If you use any kind of nicotine product, you’re at a much greater risk of developing cancer (especially lung cancer), heart disease, and respiratory diseases. It doesn’t matter how long you’ve smoked, you can significantly reduce your risk of health problems by stopping smoking. Get in touch with one of our therapists today and we’ll help you on the road to becoming completely smoke-free.